- As mentioned here, same bit pattern can represent different things depending on the context, like the program reading the bit pattern, etc.
Representing integers
- A typical program may either be dealing with unsigned integers or signed integers.
- The following image shows the representation of various values for different word sizes, :
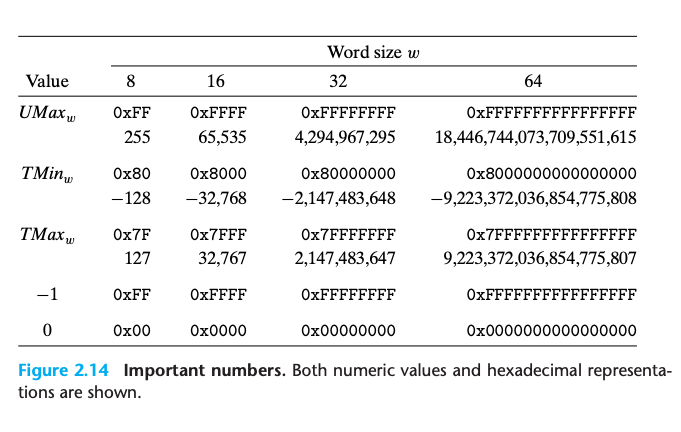
Same bit pattern encode different data - context matters
-
The following table gives the two’s complement representation of and , and the unsigned representation of . Notice that the bit pattern of and are identical.
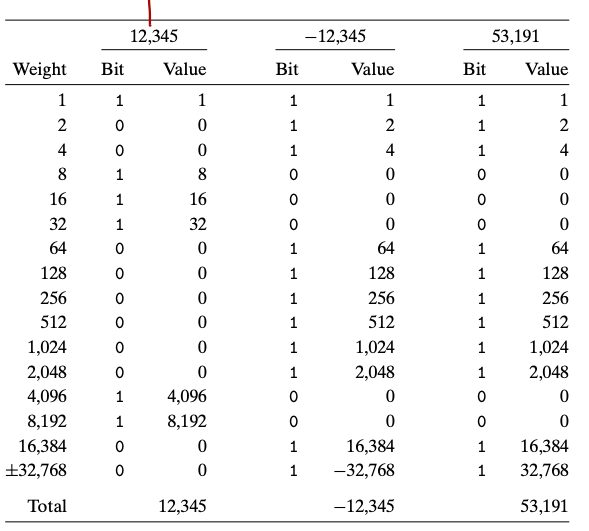
-
The same bit pattern can be read as an unsigned integer as well as a two’s complement integer. This happens when we perform type casting between the two data types. Read more about these conversions here