Requirements
- Size of a key-value pair is small - less than 10 KB
- Ability to store big data
- High availability - System responds quickly, even during failures
- High scalability - System can be scaled to support large data
- Automatic scaling - Addition/Deletion of servers should be automatic based on traffic
- Tunable consistency
- Low latency
We will designing an AP system
Partitioning of data
- To store big data, we will need to partition the data into smaller partitions and store them in multiple servers
- Consistent hashing can be used to partition the data as it provides these benefits:
- Evenly distribute data
- Minimize data movement when nodes are added/removed
- Virtual nodes can be used to ensure heterogeneity. Servers with higher capacity can be assigned more virtual nodes
Ensuring high availability and reliability
Assuming that we are using consistent hashing
- To ensure high availability and reliability, data needs to be replicated across servers, where is a configurable parameter.
- We can replicate data easily on the hash ring across nodes
Taking care of consistency
- Since data is now replicated across nodes, it must be synchronized across all replicas to ensure high consistency.
- We can use a technique called Using Quorum Consensus to get consistency to guarantee consistency for both read and write operations
- In this example, we will be trying to achieve eventual consistency
Resolving conflicts/inconsistencies
- Replication gives high availability but causes inconsistencies among replicas
- We will use versioning and vector clocks to detect and resolve inconsistencies
Handling failures
- Failures can be detected using gossip protocol
- Use sloppy quorum to improve availability after the failure is detected
- Recovering from temporary failures - Hinted handoff
- Recover from permanent failures - Merkle Trees
High level architecture
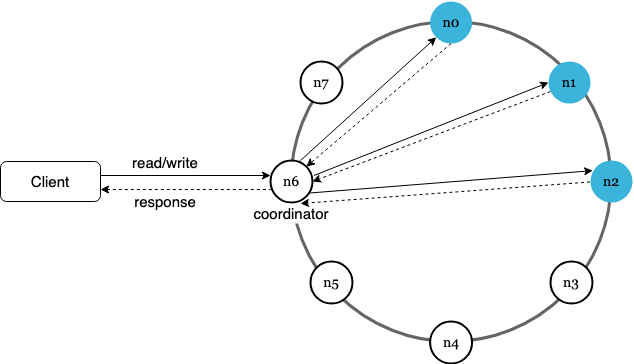
- Clients communicate with the key-value store through APIs:
get(key)andput(key, value) - Coordinator is a node that acts as a proxy between the client and the key-value store
- Nodes are distributed on a hash ring
- System is completely decentralized - adding/removing nodes can be automatic
- Data is replicated at multiple nodes
- No single point of failure as every node has the same set of responsibilities
Related Notes
- Scaling a web app
- Consistent hashing
- Virtual nodes in consistent hashing
- Meaning of availability in distributed systems
- Replicating data on the hash ring