Simple setup
How does a web request happen in a simple single-server setup?
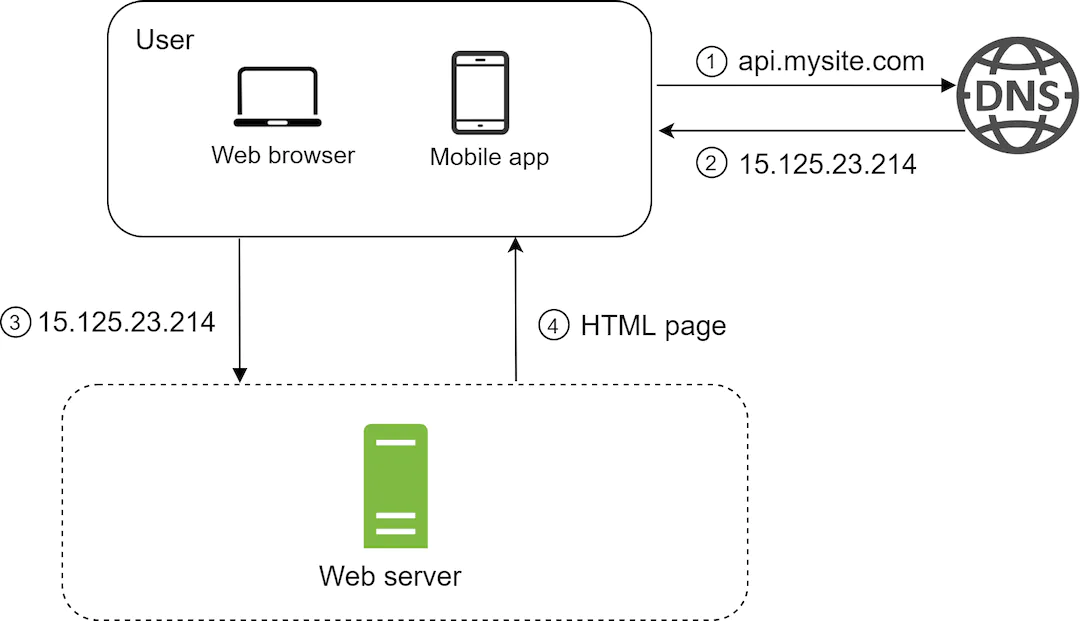
Step 1: Separating the data and web tier
Separating web traffic (web tier) and database (data tier) servers allows them to be scaled independently
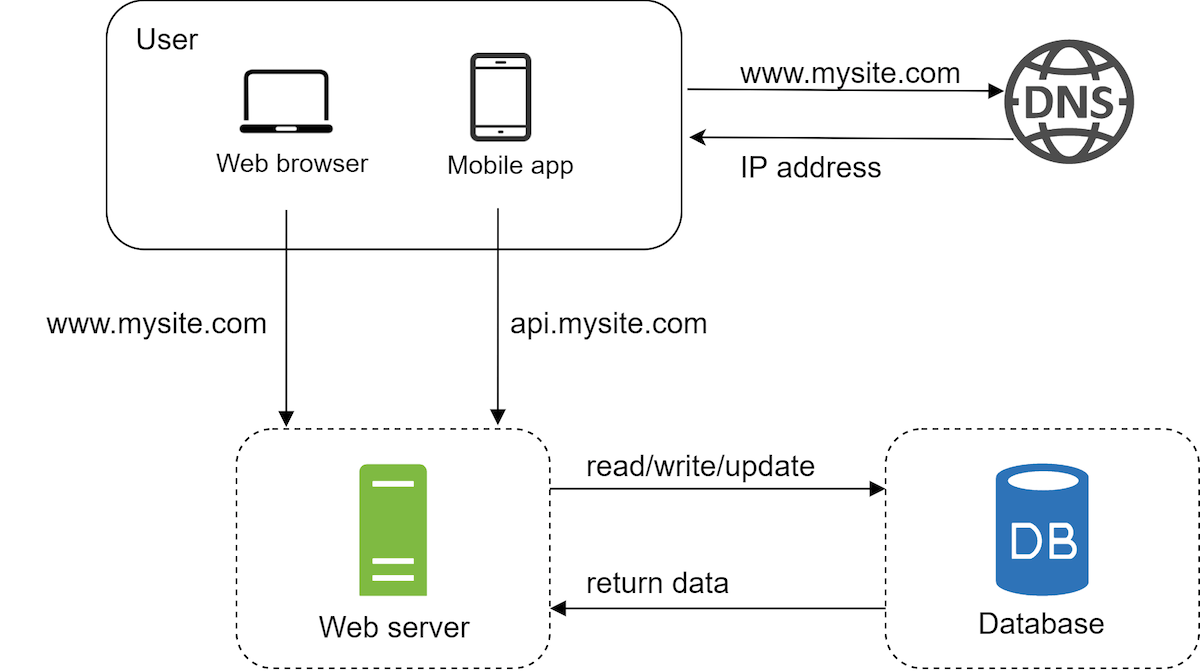
Which database to choose?
There are, primarily, two kinds of databases:
Step 2: Multiple web servers - Using load balancer
- Users will send requests to the public IP of the load balancer, which in turn will decide which server to forward the request to
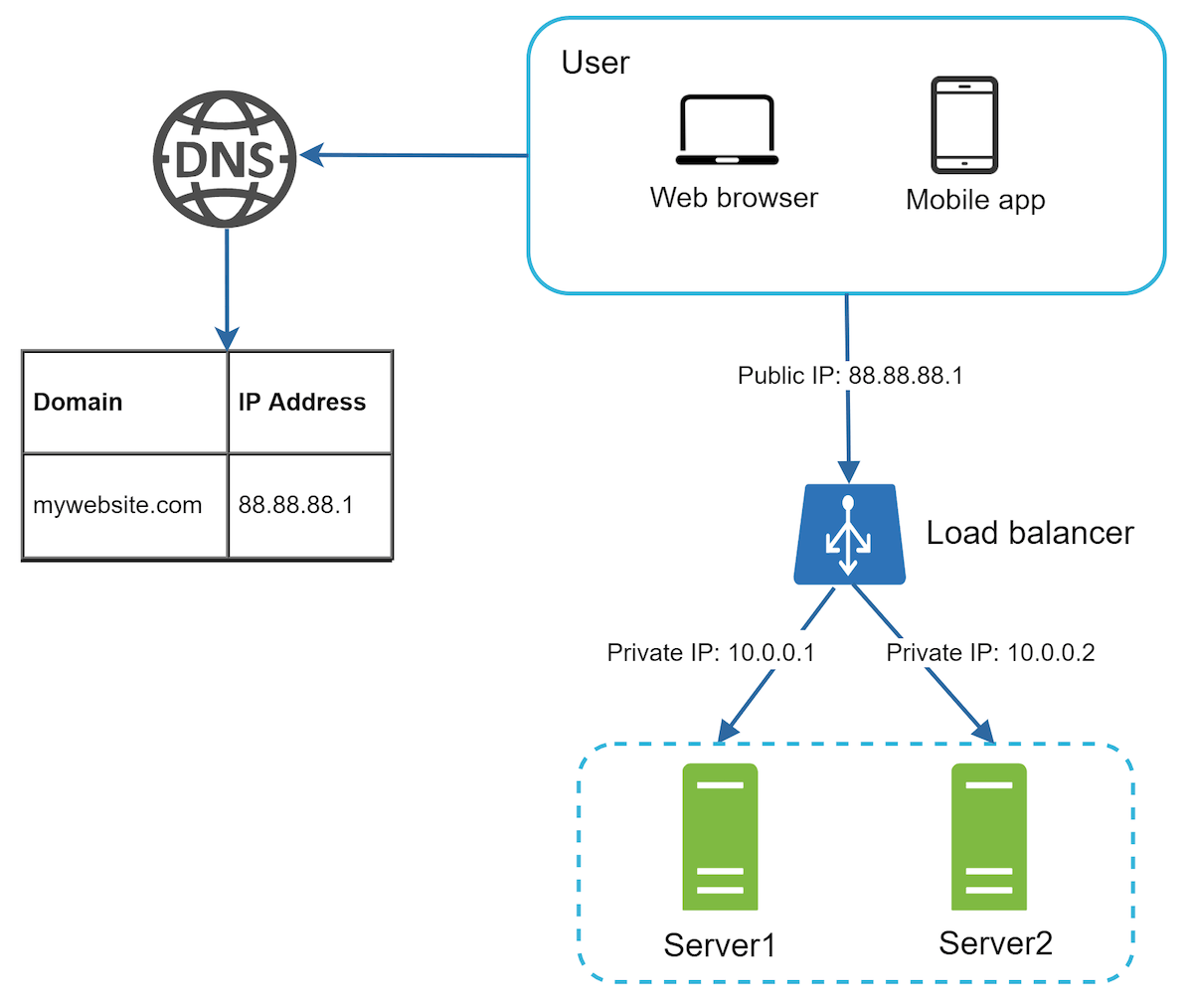
- If the traffic increases, the number of servers can be increased and the load balancer can start sending the increased requests to the new servers too.
Step 3: Replicating data
- Replicating data is important in order to ensure that all data is safe in the event that our main DB server goes down
- A common way is to perform database replication using master-slave relationship
Step 4: Inserting a cache tier
- Used in order to improve the data fetch speed of frequently read data
- In this scenario, we will go with the Read-through cache
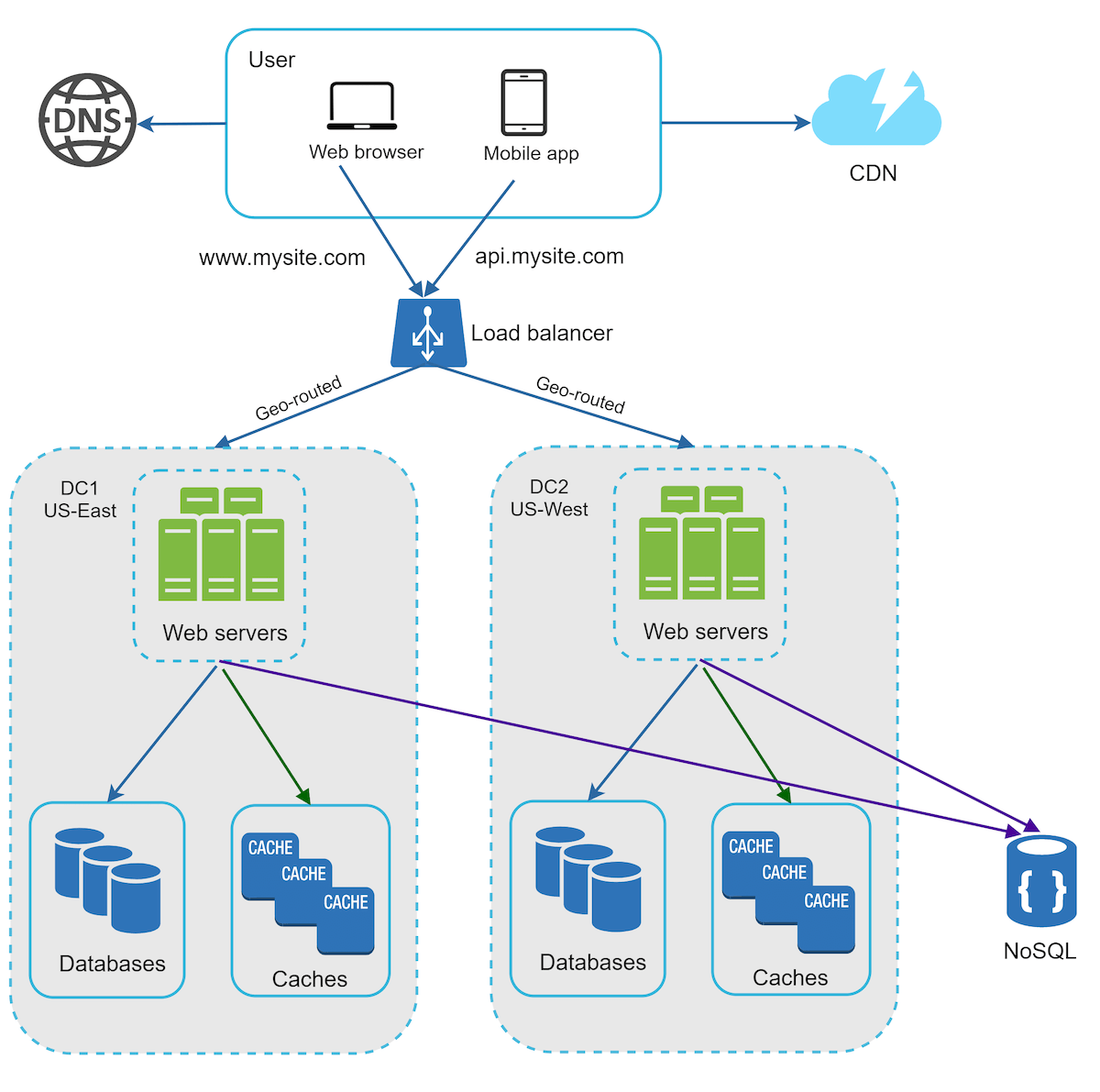
Step 5: Using a CDN
- Used to deliver static content
Step 6: Scaling horizontally - Create stateless web tier
- We need to move state (like user session data) out of the web tier
- Good practice is to store session data in the persistent storage such as relational database or NoSQL
- Each web server in the cluster can access state data from the persistent storage created above
- This gives us the Stateless web server
Step 7: GeoDNS routing users
- Data centers are replicated across regions
- Users are geo-routed to the closest data center
Step 8: Decoupling systems to support independent scaling of systems
- Message queues help with decoupling of systems reducing inter-service dependencies
Step 9: Logging
- Monitoring logs is important in order to identify errors and problems in the system
Step 10: Collecting metrics
Collecting application system metrics
Step 11: Automating application development process
Automating application maintenance cycle
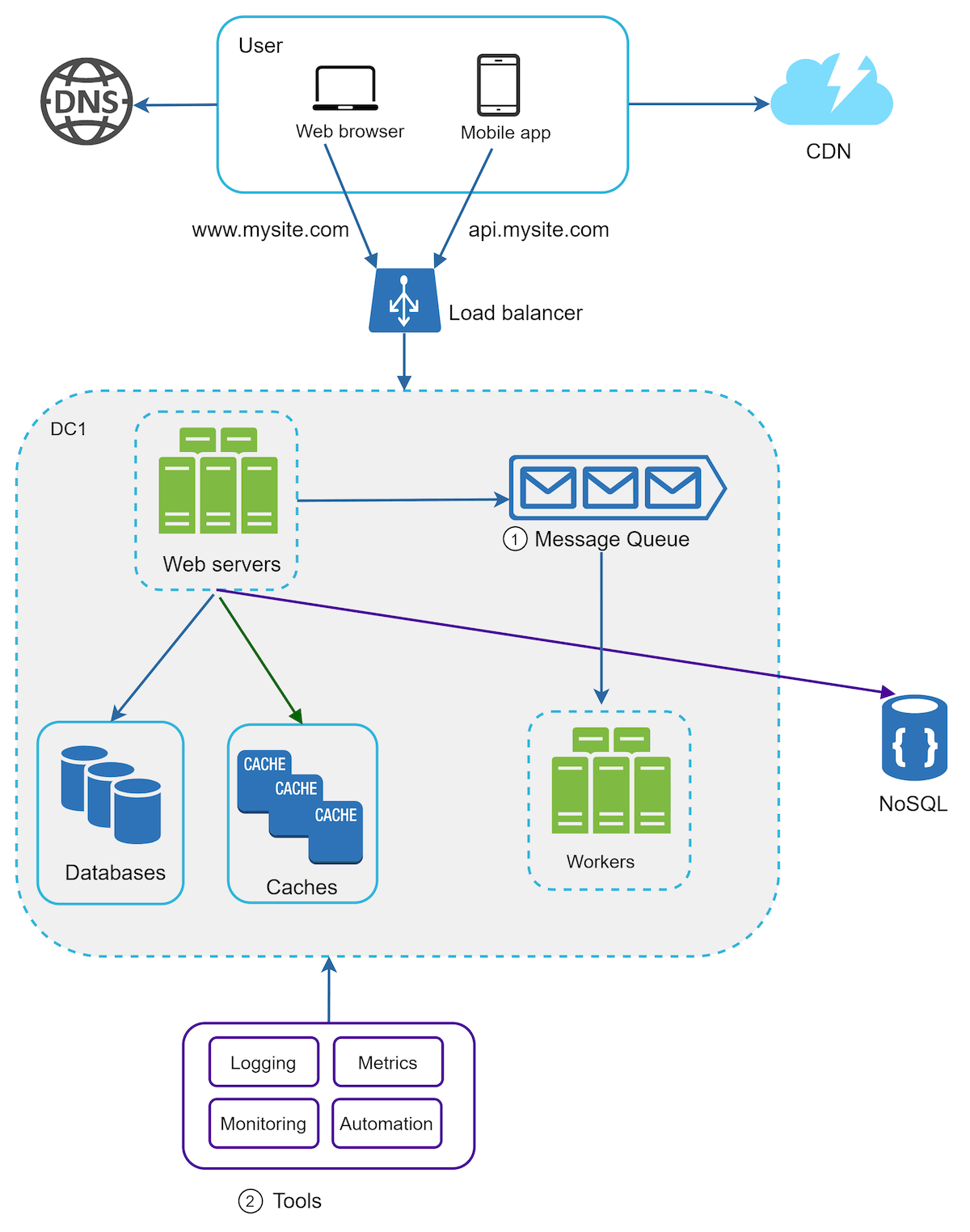
Step 12: Scaling the database
- Can be done using:
- Can also vertically scale the database
- Database sharding